pelvic compression test meralgia paresthetica|meralgia paresthetica surgery and recovery : member club Meralgia Paraesthetica (MP), also known as Bernhardt-Roth or LFCN (lateral femoral cutaneous nerve) neuralgia, comes from the Greek term meros (thigh) and algos (pain) meaning thigh . Biografia. Filha de Artur Sampaio Carepa e de Maria José de Vasconcelos Carepa, Ana Júlia Carepa nasceu em Belém do Pará em 23 de dezembro de 1957. [5]Formada em arquitetura pela Universidade Federal do Pará (1976-1980), em 1981 Ana Júlia começou a trabalhar no Banco do Brasil e tornou-se diretora do Instituto de Arquitetos do Brasil, .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Gratuitos - Maikelly Muhl | Site Oficial
This video is for educational purposes only. Do not act on this video or self diagnose without consultation of your primary medical provider. .. Special thanks to the below authors for this . They’ll perform a thorough physical exam, including a hands-on test called a pelvic compression test. During this test, your provider will apply pressure on your thigh to rule .Meralgia Paraesthetica (MP), also known as Bernhardt-Roth or LFCN (lateral femoral cutaneous nerve) neuralgia, comes from the Greek term meros (thigh) and algos (pain) meaning thigh . Diagnostic maneuvers include the pelvic compression test in which the patient lies on their unaffected side, and the examiner applies downward pressure on the patient’s .
The pelvic compression test is a sensitive and specific test for MP, helping to distinguish it from lumbosacral radicular pain. Most patients with this condition can be managed successfully with .
The pelvic compression test is usually positive (this involves deep palpation in the groin). There should be no signs of muscle weakness. Radiology such as ultrasound imaging, X-ray, CT scan or MRI of the hip and pelvic area may be . For most people, the symptoms of meralgia paresthetica ease in a few months. Treatment focuses on relieving nerve compression. Conservative measures. Conservative .Clinical tests to evaluate MP include the pelvic compression test, the femoral nerve neurodynamic test, and nerve blocks using lidocaine or procaine.The pelvic compression test is a sensitive and specific test for MP, helping to distinguish it from lumbosacral radicular pain. Most patients with this condition can be managed successfully with .
Pelvic compression test Turn patient on side; Compress pelvis; If symptoms are relieved after 30s of lateral compression diagnosis is confirmed; Differential Diagnosis . Meralgia paresthetica; Septic arthritis. Septic arthritis of the hip (peds) Obturator nerve entrapment; Avascular necrosis of hip; Thigh Numbness. A cause of thigh pain, meralgia paresthetica can be mistaken for other conditions. Careful history can identify this mononeurapthy. . results, the pelvic compression test has a sensitivity of diagnosing MP of 95%. The . The pelvic compression test is highly sensitive and the diagnosis can often be made with this test alone. 7. . Meralgia paresthetica-like syndrome may be caused by transient lumbar nerve root injury without definite compression: a case report. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010 Dec;93 Suppl 7:S307-10.Part 1 addressed rucksack palsy and digitalgia paresthetica; here, meralgia paresthetica (MP) is discussed. . and may be relieved by adopting other postures. Clinical tests to evaluate MP include the pelvic compression test, the femoral nerve neurodynamic test, and nerve blocks using lidocaine or procaine. . Options include identifying and .
Laboratory pulp dehydrator exporting
What causes meralgia paresthetica? Meralgia paresthetica is caused by irritation of the nerve, most commonly from entrapment. The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, which runs through the pelvis, groin and into the thighs, can become compressed due to swelling, trauma or pressure in the surrounding areas. Common causes of meralgia paresthetica . Diagnostic maneuvers include the pelvic compression test in which the patient lies on their unaffected side, and the examiner applies downward pressure on the patient’s ilium/pelvis for approximately 45 seconds. A test is positive if symptoms are reduced and has a reported sensitivity and specificity of 95% and 93%, respectively.Meralgia paresthetica (MP), an entrapment of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN), presents with a localized area of pain, paresthesia, or numbness on the anterolateral region of the thigh. . The other clinical parameters of the patients such as sense, pelvic compression test, leg length discrepancy, tenderness, Tinel sign, .
Meralgia paresthetica (MP), a neuropathy of the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (LFCN), is an uncommon cause of neuropathic thigh pain. . The Pelvic Compression test and Neurodynamic Testing can also be used to help the diagnosis during clinical exam. Image 2. Demonstration of the pelvic compression test (courtesy of researchgate.net) Meralgia paresthetica. Meralgia paresthetica is a condition that causes tingling, numbness and burning pain in the outer part of the thigh. The condition is caused by compression of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, which supplies feeling to the upper leg. . Common causes of this compression include any condition that increases pressure on .Download scientific diagram | Pelvic compression test. The patient is side lying with the uninvolved side on the examination table. . Objective To present a unique case of meralgia paresthetica .
Meralgia paresthetica is a mononeuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN), most commonly caused by entrapment as it passes underneath the inguinal ligament. . Pelvic Compression Test (see photo below) With patient in side-lying position, press downward and slightly forward, in a manner to slacken the inguinal ligament – hold .
Home Meralgia Paresthetica – Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Neuropathy pelvic compression test. pelvic compression test. Download article as PDF. Photo is courtesy www.sportinjuriesandwellnessottawa.blogspot.com. Search This Site. Social Counter. 47 Followers Follow. 12,200 Subscribers Subscribe.A physical exam may include tracing the exact location of pain and numbness. Strength testing, reflex testing, and sensation testing of the affected thigh can help with making a proper diagnosis of meralgia paresthetica. A pelvic compression test will likely be completed, which involves applying pressure on the thigh. Meralgia paraesthetica is a nerve (neurological) condition that causes pain in the outer thigh. It is caused by compression of a nerve. Written by a GP. . growths (tumours) on a nerve. Pelvic or intra-abdominal tumours (including cancerous ones) could also compress the nerve and cause this problem. . Meralgia Paresthetica. Curr Pain . Meralgia Paresthetica - Download as a PDF or view online for free . The Pelvic Compression Test The pelvic compression test is a diagnostic tool that involves placing the patient in the lateral recumbent .
Meralgia paresthetica is a painful compressive neuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN), causing burning pain and paresthesia in the anterolateral thigh. . Pelvic compression test positive (sensitivity of . ABSTRACT. Meralgia paresthetica (MP), coined from the Greek words meros (thigh and algos), meaning pain, is a neurological disorder characterized by a localized area of paresthesia and numbness on the .A positive pelvic compression test and Tinel's sign can be used to identify those with lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment. 30 The pelvic compression test involves applying a downward force to the pelvis with the patient's symptomatic . Meralgia paresthetica: a review of the literature. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8:883-893. [PMC free .
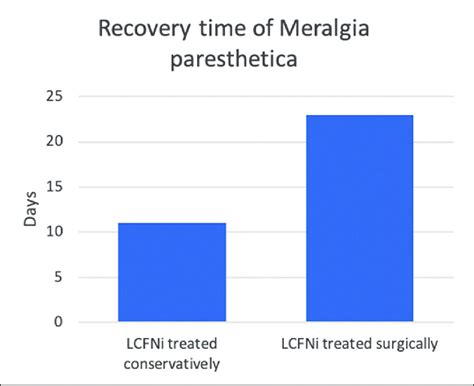
meralgia paresthetica surgery and recovery
meralgia paresthetica right lower limb
While the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve experiences compression with meralgia paresthetica. The inguinal ligament frequently entraps the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. . Pelvic Compression Test: Your doctor will apply pressure to your thigh during this exam to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms. Other simple touch and reflex . The pelvic compression test can also help with diagnosis. One very small study showed > 90% sensitivity and specificity. . Parisi, Mandrekar, Dyck, Klein. Meralgia paresthetica Relation to obesity, advanced age, and diabetes mellitus. Neurology. 2011 Oct 18; 77(16): 1538–1542. Thanks to Dr deSouza, Dr Tu, and Dr Valesky for their input in .In meralgia paresthetica, swelling, trauma, or pressure can narrow these openings and squeeze the nerve. When this happens, you may experience pain, paralysis, or other dysfunction. . You may need both an abdominal and/or a pelvic examination to exclude any problems in those areas. . The goal is to remove the cause of the compression. This .
Meralgia paresthetica (MP) is caused by entrapment or injury to the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (LCNT), known as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. . pelvic compression test, and LCNT nerve block are commonly used diagnostic tools. Neurophysiologic studies and imaging may narrow the differential diagnoses. If conservative . Meralgia paresthetica is a compressive neuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Surgery is the gold standard for severe cases. However, no high-quality evidence exists on which strategy is best: decompression or neurectomy. . The diagnosis of MP was made based on clinical symptoms and signs: the Pelvic Compression Test and Tinel at .
Background: The effectiveness of the muscle energy technique (MET) on postpartum meralgia paresthetica (MP) . Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve distal latency, pain intensity, response to the prone knee bend (PKB) test and pelvic compression test were assessed. Results: Patients allocated to the MET group had improvements compared to the . Meralgia paresthetica is a neurological condition that causes numbness, tingling, and sometimes pain in the outer thigh. . This results from nerve compression and is usually not serious .
Meralgia paresthetica is a condition that causes tingling, numbness and burning pain in the outer thigh. It’s caused by compression of the nerve that provides feeling to the skin covering the thigh. Meralgia paresthetica also is known as lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment. . But images of your hip and pelvic area might be helpful to . The pelvic compression test is a sensitive and specific test for MP, helping to distinguish it from lumbosacral radicular pain, and most patients with this condition can be managed successfully with conservative measures and those requiring surgery can be treated effectively with nerve decompression. Expand
Differential Scanning Calorimeter exporting
Race Bootcamp. Race Bootcamp. 3,401 likes · 11 talking about this · 176 were here. Treinos de alta intensidade que vão te viciar⚡️.
pelvic compression test meralgia paresthetica|meralgia paresthetica surgery and recovery